
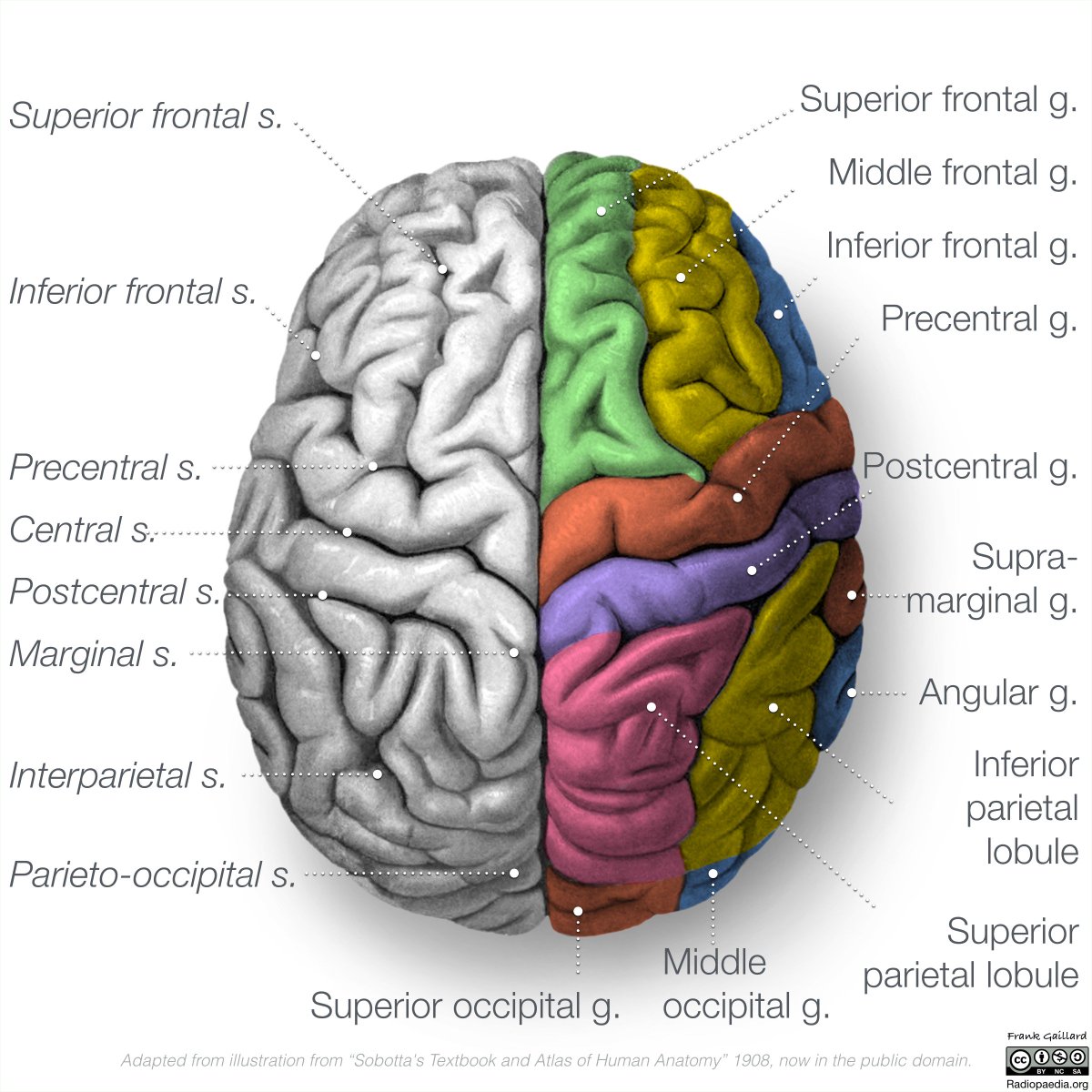
The central sulcus separates the frontal and parietal lobes, with the lateral sulcus separating the frontal and temporal lobes. It sits atop the temporal lobe, in front of the parietal lobe, and apart from the occipital lobe, with portions of the limbic system-sometimes called the limbic lobe crossing all four brain lobes, including the frontal lobe. Named for its location, the frontal lobe is situated toward the front of the cerebrum, just behind the forehead and under the frontal skull bones. The frontal lobe plays a key role in this complex set of cognitive functions. The cerebrum is the newest part of the brain to have evolved, and houses most “higher” functions, such as conscious thought, morality, memory, and the ability to learn through memorization, deduction, and other complex processes. Neuroscientists have traditionally divided the brain's cerebrum into four lobes: the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal. This part of the brain is the newest from an evolutionary perspective, and is the last to develop, making the frontal lobe both highly malleable and susceptible to developmental damage. It plays a role in everything from movement to intelligence, helps us anticipate the consequences of our actions, and aids in the planning of future actions. If you look at how humans bond with their mates and care for their young, you'll see some surprising similarities between us and other species.The frontal lobe is the home of much of what makes us human. But they have learned more about how the feelings that occur when people "bond" are produced in the brain.
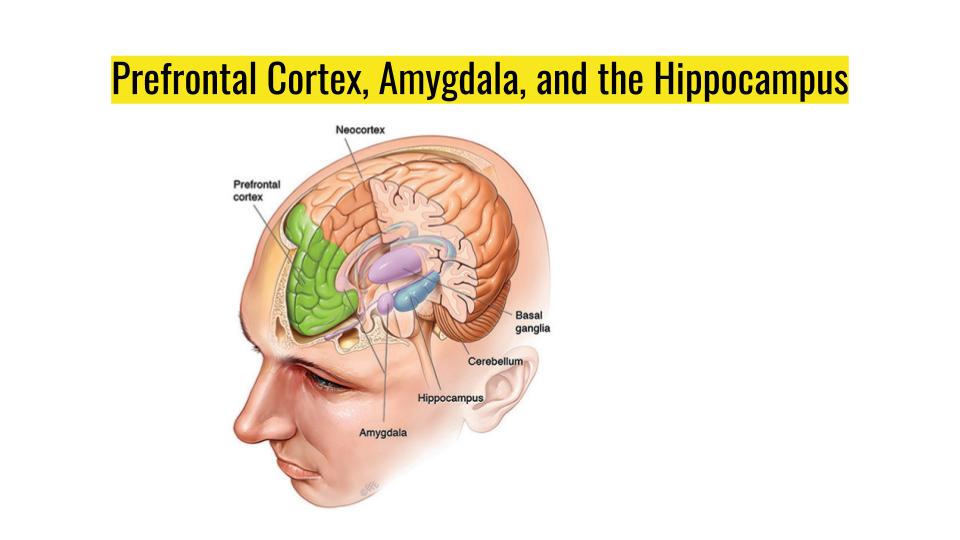
What is love? Neuroscientists can't answer that question yet. What happens to the brain when an antidepressant is introduced? What other practices can be implemented to combat depression? Love These drugs, called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), increase levels of serotonin in the synapse by blocking its removal. Millions of Americans take antidepressant drugs that alter how the brain processes serotonin, a neurotransmitter linked to feelings of serenity and optimism. Together, these parts-the brain stem, cerebellum, and basal ganglia-are casually referred to as your "lizard brain." How are mammals different from lizards? Fighting Depression These parts handle basic body functions like breathing, balance, and coordination, and simple survival urges like feeding, mating, and defense. Lizards and humans share similar brain parts, which they inherited from fish. While all mammals produce basic emotions like fear and anger, humans have especially highly developed social emotions, such as shame, guilt, and pride, which involve an awareness of what other people think and feel about us. When you're feeling an emotion, it's often written all over your face. When the danger subsides, your brain sends out a calming signal in the form of chemicals that dampen the response of regions that create fear. If you're in danger, for example, your brain releases stress hormones that make you react faster, flooding certain regions with the neurotransmitter epinephrine (adrenaline). By layering signals on other signals, your brain can adjust how you respond to things and can effectively alter your mood.
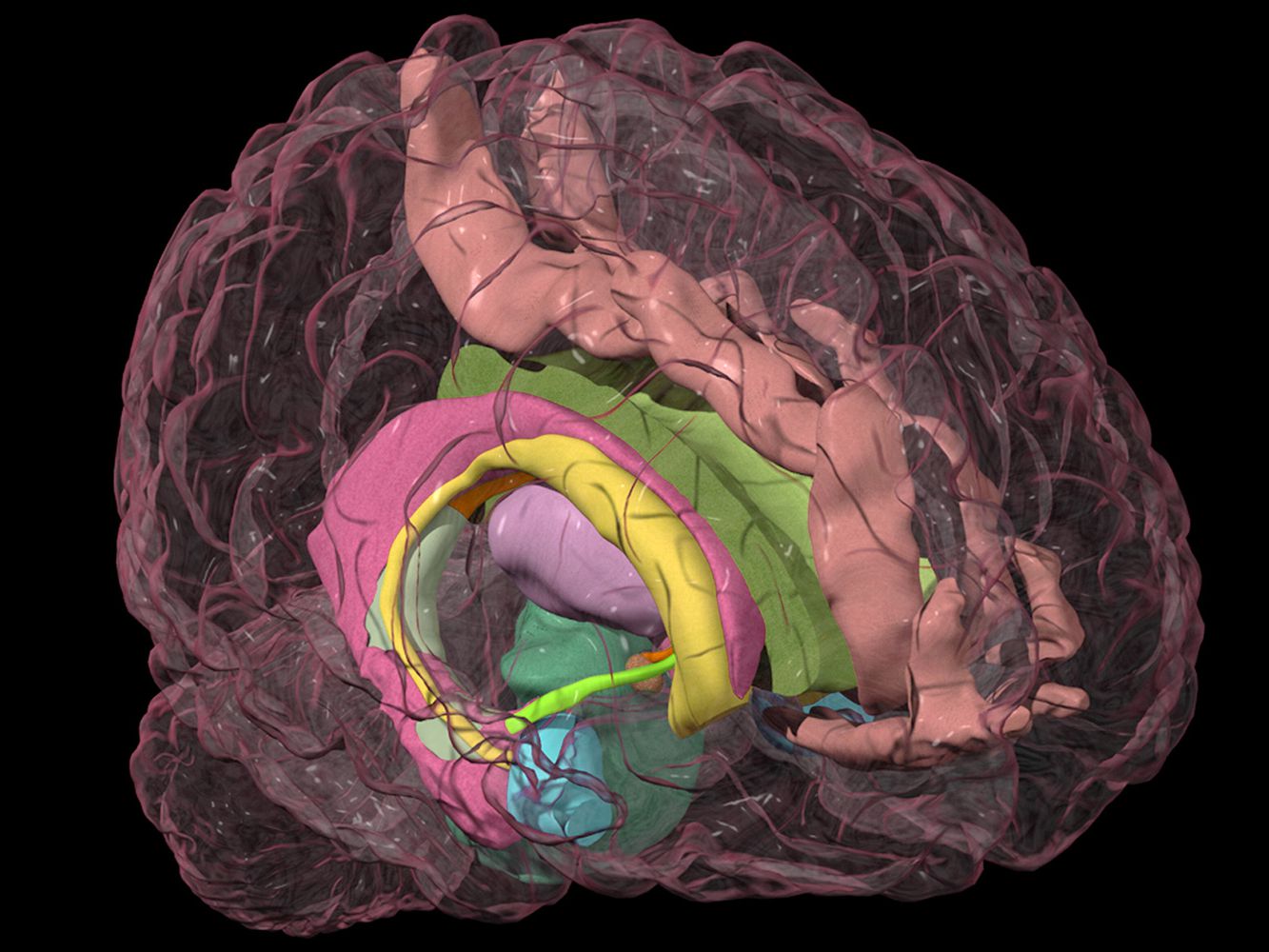
Some of these neurotransmitters go between individual cells, while others are broadcast to entire brain regions. At any given moment, dozens of chemical messengers, or neurotransmitters, are active. Emotions are controlled by the levels of different chemicals in your brain, but there is no one "love" or "hate" chemical.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
